Summary
Some of the cardiac conditions in the past required open, incisional surgery, or Minimally Invasive Surgeries. Both these types of procedures have their own limitations and affect the outcome, or recovery-time for patients. In recent years, Robotic Surgery has emerged as an excellent alternative to open or MI surgeries. The precision and dexterity possible with Robotic Surgeries helps achieve better outcomes for complex procedures, making it a win-win for both surgeon and patient. In this article, we will learn more.
Introduction
In an earlier article, we have covered the history of Robotic Surgery and market players who are innovating or expanding this domain. We also covered. In this article, we will focus on Cardiac conditions.
Robotic Surgery for the heart offers many advantages compared to open-incisional as well as endoscopic surgeries. Given the small size of the heart, tight space in the chest cavity, and the wide variety of heart conditions, robotic surgery is the most powerful tool in the hands of a cardiac surgeon, today. He/she can perform both beating heart and non-beating heart surgeries using Robotic systems. Some of the advantages are:
- Greater precision: Robotic surgery helps the surgeon operate surgical instruments with much more precision than is possible in MI or open surgeries. Thanks to high-definition, high-magnification (10x) cameras and various surgical tools. This results in fewer complications or risks, and more positive outcomes.
- Less invasive: Like MI surgery, robotic surgery is also less invasive than open surgery, and further, incisions made are small. So, this means, there is less injury or trauma to the patient’s heart and surrounding tissues. This also means less bleeding, less pain, less scarring and faster recovery.
- Improved visualisation: Video cameras used in Robotic surgery are high-resolution (10x magnification) and can rotate on various axes, over large angles. The high-quality, 3D images help the doctor visualize the site better, which results in quick and better decision-making, quick and better interventions.
- More dexterity: Robotic arms used in Robotic surgery can rotate and bend in various angles, with a large range of controlled motion. Combined with specialized instruments, the surgeons can perform complex manoeuvres with ease, compared to open or MI surgery.
- Reduced Risk of Infection: Because of the minimally-invasive nature of robotic surgery, there is less contact with, or exposure to – multiple surfaces, thereby reducing the risk of infection compared to other forms of heart-surgery, where infection is inevitable.
- Shorter Hospital Stay: Since healing and recovery is fast, patients can be discharged in a couple of days which improves their comfort, and reduces the overall cost.
Cardiac conditions treated using Robotic Surgery
There are various conditions, for which the candidate is well-suited for Robotic Surgery. Depending on the age, medical history, current health status, lifestyle and severity of the condition, some patients may not be a candidate for Robotic Surgery. The doctor will take a call in this regard after thorough examination. However, most patients are suited for this.
All the conditions listed below are treated using the da Vinci Surgical System, although in recent years, competitive products are also being used.
- Mitral valve operations: The mitral valve, also called the bicuspid valve, is located between the left atrium and left ventricle. It is made up of 2 flaps which open, and shut tight, to allow blood-flow in one direction, and prevent blood-flow in the opposite direction. Over time, in some people, the wear and tear of this valve causes the valve to not open or close efficiently resulting in blood-leakage. Or the flaps become stiff due to various reasons and do not close on time. Sometimes, the valve defect can be repaired while in some cases, the valve must be replaced with a new one. Previously, such repair or replacements were done using open or MI surgeries. Robotic surgery takes the advantages of MI surgery to the next level, making valve repair or replacement quick, efficient, and more precise.
- Correction of atrial septal defect: Atrial septal defect is a congenital (present since birth) condition in which there is a tiny hole between the atria or upper chambers of the heart. This can cause the lungs to overfill with blood and also overwork the right chambers of the heart. The right side will grow large and eventually become weak. Even the pressure in the lungs increases, causing pulmonary hypertension. In the past, open surgery and later, MI surgery was done to plug the hole with a mesh, after which tissue will grow around the mesh and strengthen the plug. The same procedure can be done easily using Robotic Surgery.
- Intracardiac tumour resection: Like with any other part of the body, tumours can develop inside the heart too. Depending on the exact location, and severity of the condition, this can lead to various symptoms and consequences such as high temperature, unexplained weight-loss, constant fatigue, muscle aches, fever and night sweats, cough, leucocytosis (increase in WBC count), embolisms (blocked arteries), arrhythmias (irregular heart-rhythm), haemorrhagic pericardial effusion (an abnormal build-up of fluid in the pericardial cavity), heart failure, dyspnoea (shortness of breath), cardiomyopathy (disease of the heart-muscle) and superior vena-cava syndrome. Now, Robotic Surgery is performed to resect or remove the tumour growths.
- Pericardiectomy: The pericardium is a fibrous, bag-like sack that encloses the heart and major blood-vessels. It also helps o separate the heart from lungs and other parts of the chest cavity. In some people, the pericardium may become fibrous, or calcified, or develop granular tissue which makes the pericardium rigid leading to improper ventricular filling of blood. Pericardiectomy is a procedure in which some part of, or the entire pericardium is removed. While open and MI surgeries were previously the options, today, the same procedure can be successfully performed using Robotic Surgery.
- Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation (Afib): Atrial fibrillation is a condition in which the heart beat is irregular and very fast. It can cause poor blood-flow and lead to blood-clots in the heart. The person may experience fatigue, shortness of breath, palpitations, fluttering heart, chest pain (angina), dizziness, headache and swooning (syncope). Surgical treatments for Afib are aimed at resetting the heart-rhythm and includes electrical cardioversion, pulmonary vein ablation, a permanent pacemaker, left atrial appendage closure and the MAZE procedure. All of these can be done using Robotic Surgery now.
- Totally Endoscopic Coronary Artery Bypass (TECAB): TECAB is one of the various methods of revascularization, done to overcome blockages in the coronary arteries of the heart. CABG (Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting) and OPCAB (Off-pump Coronary Artery Bypass) are some of the other methods. Instead of making a long incision through the breastbone, which is what is done in an open surgery, TECAB involves making use of 4 to 5 small incisions, and the procedure is completed robotically using the da Vinci Surgical System.
- Treatment of Aortic conditions: There are nearly 17-18 conditions that affect the aorta, which is the largest artery in the body, and which supplies pure blood to the body. In recent years, experiments have been done to treat some of these conditions using Robotic Surgery. More recently, a hospital in India successfully performed an aortic valve replacement using Robotic Surgery.
How is the procedure done?
- After conducting preliminary tests and general checkup, the doctor will seek the patient’s consent and schedule the procedure.
- Women who are pregnant should mention this to the doctor.
- If the person is taking blood-thinners, or any medication, including homeopathic and ayurvedic medicines, he/she must mention this to the doctor.
- If the person smokes, he/she should stop smoking a week before the procedure.
- The previous night of the procedure, the person must not consume anything after midnight.
- On the day of the operation, the patient will be given a mild sedative to help him/her relax.
- Then he/she will be wheeled into the operating theatre and anaesthetized (general anaesthesia administered). A tube will be inserted into the patient’s throat to help him/her breathe.
- A cardiopulmonary bypass machine (heart-lung machine) will be connected in most of the cases.
During and after…
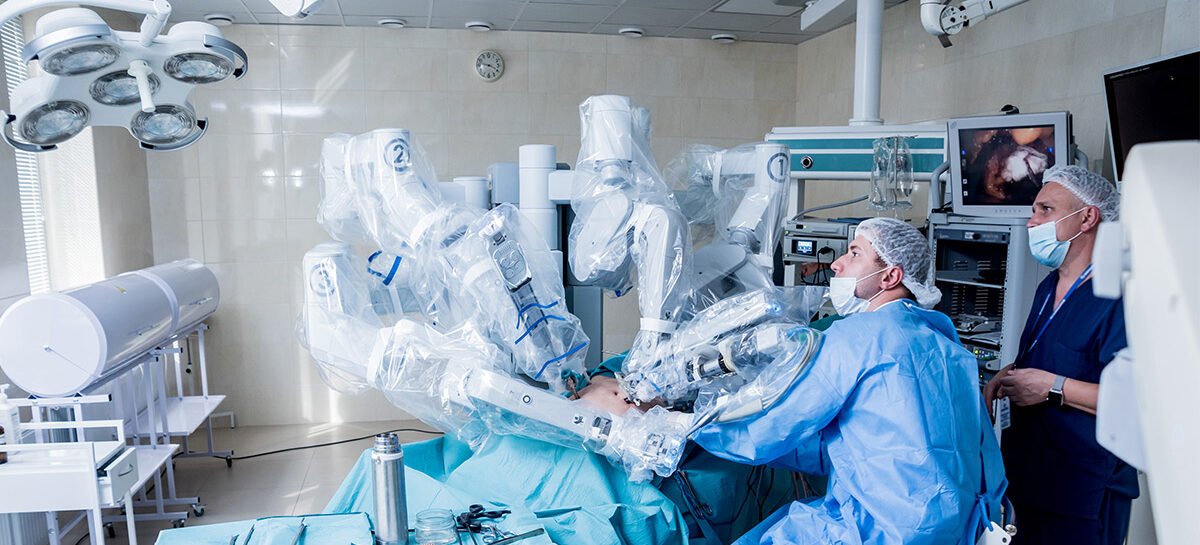
- The surgeon will make several, small incisions in the side of the chest, in line with the gaps between every pair of consecutive ribs.
- Robotic arms of the da Vinci system are inserted into these incisions. These arms carry surgical instruments as required for that intervention, at the tip.
- The high precision camera will be inserted into another incision.
- The surgeon will take his seat at the computer console and manipulate the camera and robotic arms as required.
- Next, he/she will make the necessary interventions.
- Once the procedure is completed, the robotic arms and camera will be withdrawn.
- The surgical team will dress up the incisions and move the patient to the ward.
- The patient will stay in the hospital for a couple of days and will be closely monitored, after which he/she will be discharged.